Plan and Scope the Pentest
Set the start date for your pentest and define its scope.

In the fourth step of the pentest wizard, you can:

Schedule the Pentest
Depending on your PtaaS tier, you can schedule pentests with a start date from at least one to three business days after submitting it for review. Pentests submitted after 11 AM PST (19:00 UTC) will require an additional business day start time.
If you have any special requirements, such as qualifications for pentester certifications, we reserve the right to start the pentest later than the flow time specified in your PtaaS tier.
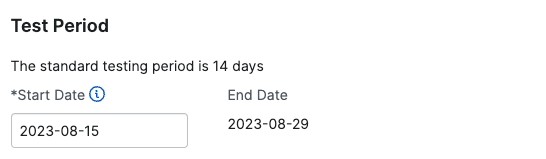
Pentest Timelines
Pentest timelines depend on the pentest type, scope, and other factors. When you schedule your pentest and set a start date, the end date populates automatically.
Standard pentest timelines:
- Comprehensive Pentests: 14 days
- Agile Pentests:
- 3 or 4 credits: 7 days
- From 5 credits: 14 days
Learn more about the pentest types.
Important
Pentest duration may vary depending on the pentest scope and other factors. Pentests must be completed before your contract ends. We are unable to conduct pentesting outside of your subscription period.Scope the Pentest
The complexity of your asset determines the number of credits required for a pentest. The bigger the pentest scope, the more credits you need.
A Cobalt credit is a standardized unit of work that represents 8 pentesting hours. You can think of a Cobalt credit as a virtual voucher that you consume whenever you want to run a pentest. Learn more about Cobalt credits.
Scoping a Comprehensive Pentest
When you set up a new Comprehensive pentest for an asset that you’ve already comprehensively tested earlier, you can select one of the options:
- If the general size of the asset has not changed, inherit the scope of your last completed Comprehensive pentest.
- If the general size of the asset has changed, rescope the pentest by adjusting scoping parameters, as described below.

To set the pentest scope, identify the complexity of your asset. Under Scoping, specify the number of characteristics associated with the asset that need to be tested. To get exact numbers, consult with the asset owner inside your organization.
Scoping parameters differ for each asset type:
- Web
- Mobile
- API
- External Network
- Internal Network
- Cloud Config
- Desktop
- AI/LLM Pentest
- Assets of multiple types
Once you’ve scoped the pentest, review the required credits, as determined by our algorithm.
Web
To scope a pentest for a Web asset, specify the number of the following characteristics of the asset that need to be tested.
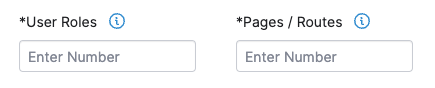
| Parameter | Definition | Scoping Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| User Roles | A User Role is a user group within an application with specific permissions, such as an administrator, manager, or guest. | Enter the number of User Roles in your Web asset that need to be tested. Determine User Roles based on personas, or target user groups of your asset. Group user permissions into several levels, and count the number of such groups. |
| Pages/Routes | A Page is a hypertext document with a unique URL that a user interacts with. Dynamic pages are most relevant for pentests.
A Route is a system for resource navigation in single-page applications (SPAs). In SPAs that use frameworks such as Angular, React, or Ember, routes provide unique URLs to specific content within the application. |
Determine the type of your Web asset:
|
Note
If the only APIs in your assets populate web pages, you may not need to set up a separate API asset. We test such APIs as part of our tests of a Web asset.Mobile
To scope a pentest for a Mobile asset, specify the number of the following characteristics of the asset that need to be tested.

| Parameter | Definition | Scoping Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Systems | An operating system (OS) is software that allows smartphones, tablets and other devices to run applications and programs. |
Enter the number of operating systems (iOS, Android, Windows Mobile, etc) in your Mobile asset that need to be tested. Native applications are built to run on a specific mobile operating system, such as iOS or Android. Non-native applications are built to run on multiple operating systems. |
API
To scope a pentest for an API asset, specify the number of the following characteristics of the asset that need to be tested.
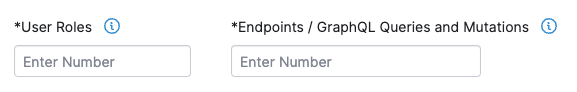
| Parameter | Definition | Scoping Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| User Roles | A User Role is a user group within an application with specific permissions, such as an administrator, manager, or guest. | Enter the number of User Roles in your API asset that need to be tested. Determine User Roles based on personas, or target user groups of your asset. Group user permissions into several levels, and count the number of such groups. |
| Endpoints / GraphQL Queries and Mutations | A RESTful API Endpoint is a URL where an API receives requests about a specific resource on its server. A GraphQL Query is a method to fetch data. A GraphQL Mutation is an operation that allows you to modify server-side data. |
We can test both RESTful and GraphQL APIs. However, these APIs work in different ways.
If you’re using API tools such as Swagger, Postman, or Insomnia to work with your API asset, you can count the number of endpoints or GraphQL queries and mutations in these tools. |
External Network
To scope a pentest for an External Network asset, specify the number of IP addresses in your external network that need to be tested.
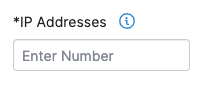
| Parameter | Scoping Guidelines |
|---|---|
| IP Addresses | Enter the number of active IP addresses in your external network that need to be tested. |
Internal Network
To scope a pentest for an Internal Network asset, specify the number of IP addresses in your internal network that need to be tested.

| Parameter | Scoping Guidelines |
|---|---|
| IP Addresses | Enter the number of active IP addresses in your internal network that need to be tested. |
If you’re working with servers on the cloud, you can also set up a Cloud Configuration asset.
Cloud Configuration
Cobalt pentesters can test services on the following platforms:
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure Cloud (Azure)
Each platform includes different categories of services, such as EC2, databases, and machine learning engines.
To scope a pentest for a Cloud Configuration asset, specify the number of the following characteristics of the asset that need to be tested.
| Parameter | Definition | Scoping Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| User Accounts, Projects, or Resource Groups | User Accounts refer to accounts in your cloud asset. Projects are all resources included in your cloud asset. Resource Groups are sets of resources in a cloud asset. |
Enter the total number of accounts, projects, or resource groups in your cloud asset that need to be tested.
|
| Unique Service Instances | Unique services are the different functionalities that you’ve configured in your cloud deployment. | Enter the number of unique services in your cloud asset that need to be tested.
|
Desktop
To scope a pentest for a Desktop asset, specify the number of the following characteristics of the asset that need to be tested.
| Parameter | Definition | Scoping Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Systems | An operating system (OS) is software that allows desktop devices to run applications and programs. |
Enter the total number of operating systems in your desktop application that need to be tested. Examples of desktop operating systems include Microsoft Windows, macOS, various Linux distributions, and others. |
AI/LLM Pentesting
Cobalt offers two levels of AI/LLM pentesting of Web related Assets.
-
LLM/AI Prompt Injection (+5 credits) Focus on testing the security of your AI systems against prompt injection attacks. These attacks manipulate the AI’s input to generate malicious output, which can compromise the system’s integrity and confidentiality.
-
LLM/AI Owasp Top 10 (+16 credits) Test your LLMs against the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10 most critical web application security risks. Ensure they’re protected against unauthorized access, data breaches, and disruptions
To scope a AI/LLM pentest specify the Number of independent LLM features to be tested.
If multiple independent features are selected, the results will be documented in the same report and findings will reported in the same pentest. If seperate reports are needed, it’s recommended to run seperate pentests for them.
AI/LLM pentests can be run both as a Comprehensive pentest (including a thorough final pentest analysis and report) and as an Agile pentest (no final report).
AI/LLM pentests are available for Web assets only.
Assets of Multiple Types
Sometimes, assets fit into more than one category. To that end, Cobalt supports pentests on assets in the following groups of categories:
- Web + API
- Web + API + External Network
- Web + External Network
- Web + Mobile
To scope a pentest for a combined asset, specify the number of characteristics for each asset type that it includes. Refer to the corresponding sections of this guide for details.
View Required Credits
Once you’ve identified the pentest scope, you can see the number of estimated credits in Credits Per Pentest. Whenever you adjust the scope, our algorithm updates the number of credits.
You can see the final number of required credits when the pentest is Planned, after we review your pentest request.
Assign a Point of Contact
Cobalt Staff may reach out to the point of contact with questions regarding the pentest.
- You can assign yourself as the point of contact.
- To assign other users, go to the Collaborators tab on the pentest page.
- Organization Owners, Organization Members, and Pentest Team Members can assign a point of contact when the pentest is in the Draft or In Review states.

Next Step
If you’re ready with your pentest, select Save & Exit. In the next screen, you can review your work before submitting the pentest.